Matcha tea, with its vibrant green color and health benefits, has gained popularity worldwide in recent years. But despite its modern appeal, this powdered green tea has centuries of tradition behind it. In this article, we will explore the origins of matcha tea, the regions where it is grown, how it is produced, and its significance in different cultures.
The Origins of Matcha Tea
Matcha tea comes from Japan, where it has been an integral part of the culture for centuries. Its origins, however, can be traced back to China, where it was used in tea ceremonies during the Tang Dynasty (618–907 AD). The practice of grinding tea leaves into a powder is believed to have been developed by Chinese monks, who consumed powdered tea as a way to stay awake during long meditation sessions.
By the 12th century, Japanese Zen Buddhist monks who traveled to China brought this tea culture back with them. Japanese monks began refining the method of producing powdered tea, ultimately developing matcha as we know it today. The tea eventually became central to Japanese tea ceremonies, symbolizing tranquility, mindfulness, and spiritual connection.
Matcha Tea Cultivation and Production
The process of cultivating matcha is intricate and involves several steps to preserve its unique flavor, color, and nutritional benefits. Unlike regular green tea, which is typically grown under direct sunlight, matcha tea plants are shaded for several weeks before harvesting. This shading process increases the chlorophyll content in the leaves, giving matcha its vibrant green hue and boosting its antioxidants.
The most prestigious matcha is grown in the Uji region of Japan, known for its fertile soil and ideal climate for tea cultivation. Other regions where matcha is cultivated include Nishio in Aichi Prefecture, and Kagoshima and Fukuoka Prefectures. However, the climate, soil, and care given to the tea plants vary from region to region, affecting the flavor profiles of the matcha produced.
Once the matcha leaves are harvested, they are steamed immediately to prevent oxidation, preserving their green color and nutritional value. After steaming, the leaves are dried and ground into a fine powder using traditional stone mills. This labor-intensive method ensures that the matcha maintains its delicate flavor and aroma.
The Importance of Quality in Matcha
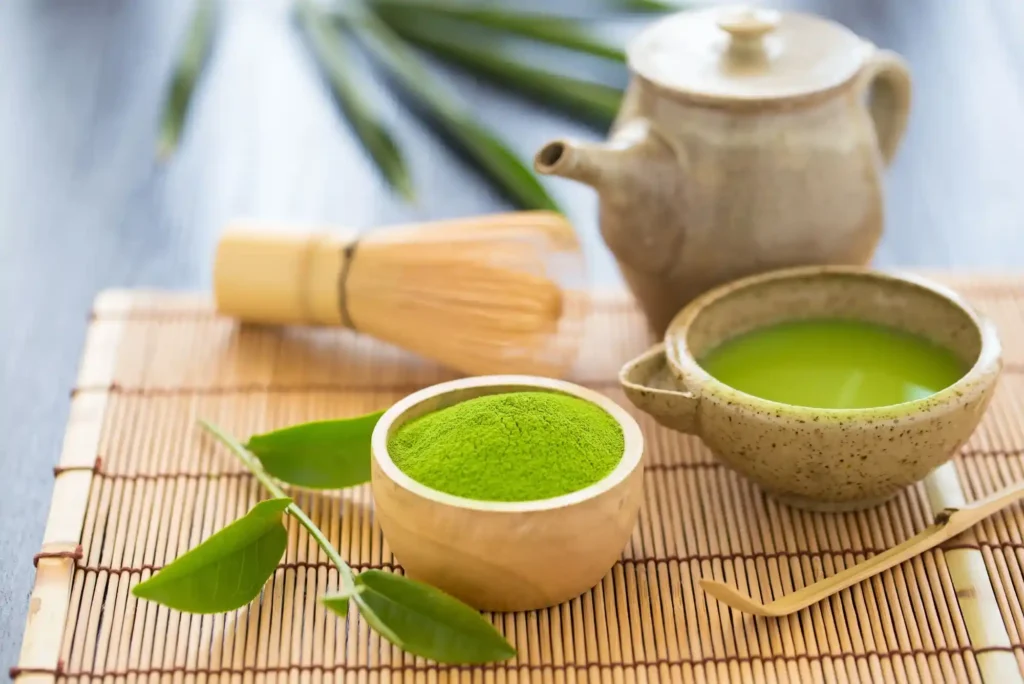
The quality of matcha depends on several factors, including the age of the leaves, the shading process, and the grinding method. High-quality matcha comes from younger, tender leaves that are carefully picked by hand. The most prized matcha comes from the first harvest, which is known for its mild flavor and vibrant color.
Matcha is categorized into different grades, ranging from ceremonial grade to culinary grade. Ceremonial grade matcha is the highest quality, used in traditional Japanese tea ceremonies. It has a smooth texture, rich flavor, and a slightly sweet taste. On the other hand, culinary grade matcha is commonly used for baking, smoothies, and other culinary applications. It has a more robust flavor and is slightly more bitter than ceremonial grade matcha.
Cultural Significance of Matcha Tea

In Japan, matcha is more than just a beverage; it is deeply embedded in the culture and spiritual practices. The Japanese tea ceremony, known as the “Chanoyu,” is a ritualistic preparation and consumption of matcha that focuses on the principles of harmony, respect, purity, and tranquility. The ceremony involves precise movements, the use of traditional utensils, and a deep appreciation of the present moment.
The importance of matcha in the tea ceremony is not only about the tea itself but also about the mindfulness and reflection it encourages. The act of preparing, serving, and drinking matcha is seen as a spiritual experience that helps practitioners connect with nature and with others. It is a practice that promotes peace, reflection, and harmony in a fast-paced world.
Outside of formal tea ceremonies, matcha is also widely enjoyed in Japan as a daily drink or as an ingredient in sweets and desserts. Matcha-flavored mochi, matcha ice cream, and matcha chocolates are popular treats in Japanese culture, showcasing the versatility of this unique tea.
Health Benefits of Matcha Tea
Matcha tea is not only loved for its unique flavor and cultural significance but also for its impressive health benefits. The process of consuming whole powdered tea leaves means that matcha provides all the nutrients found in the tea leaves, making it more potent than regular green tea.
Here are some key health benefits of matcha tea:
- Rich in Antioxidants: Matcha is packed with antioxidants, particularly catechins, which help fight free radicals and reduce oxidative stress in the body. The most notable catechin in matcha is epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), which has been linked to cancer prevention and overall health promotion.
- Boosts Metabolism: Studies suggest that matcha can help boost metabolism and increase fat burning, making it a popular drink for those looking to lose weight or maintain a healthy body weight.
- Enhances Focus and Calmness: Matcha contains L-theanine, an amino acid known for its calming effects. Combined with the natural caffeine in matcha, L-theanine helps promote a calm, focused state without the jitters associated with other caffeinated drinks.
- Detoxifies the Body: The chlorophyll in matcha helps detoxify the body by eliminating heavy metals and toxins. The high levels of chlorophyll contribute to the deep green color of matcha and support overall health.
- Supports Immune Function: The catechins and antioxidants in matcha can also help boost the immune system, supporting the body in fighting off infections and illnesses.
How to Prepare Matcha Tea
Preparing matcha tea is a simple yet meditative process. Traditionally, matcha is whisked with hot water using a bamboo whisk, known as a “chasen,” until it forms a frothy, smooth consistency. To prepare a cup of matcha:
- Sift 1 to 2 teaspoons of matcha powder into a bowl.
- Add about 2 ounces of hot water (not boiling, around 160-175°F).
- Whisk vigorously in a “W” motion until frothy.
- Enjoy your matcha tea immediately for the freshest taste.
Matcha can also be used in lattes, smoothies, and even baked goods, offering a unique flavor and nutritional boost to various recipes.
Where Does Matcha Tea Come From? – A Summary
Matcha tea is grown in Japan, with some of the most renowned cultivation regions being Uji, Nishio, and Kagoshima. The tea’s roots trace back to China, where the technique of grinding tea leaves into powder was developed. Matcha has become a symbol of Japanese culture, spirituality, and health. Today, it is enjoyed globally for its distinctive flavor and numerous health benefits. Whether consumed in a traditional tea ceremony or used as an ingredient in modern recipes, matcha continues to be celebrated for its unique qualities and significance.
Related Searches:
- Best matcha tea brands
- Matcha tea benefits
- How to prepare matcha tea
- Matcha vs green tea
- Matcha latte recipe
Reviews
People around the world have embraced matcha for its rich flavor and health benefits. Below are some reviews from matcha enthusiasts:
| Reviewer Name | Rating | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Emily R. | 5/5 | “The quality of this matcha is amazing! It’s smooth, not too bitter, and has a wonderful green tea taste. I enjoy it in my daily smoothies.” |
| David L. | 4/5 | “Great matcha for the price! The flavor is good, though it could be a little more intense for my preference.” |
| Sarah M. | 5/5 | “Matcha has completely changed my mornings! It’s energizing without the crash, and I love its health benefits.” |
People Also Ask:
- What is the difference between matcha and green tea? Matcha is made from powdered whole tea leaves, while green tea is typically brewed from loose leaves. This means matcha contains more antioxidants and nutrients than regular green tea.
- How does matcha help with weight loss? Matcha boosts metabolism and increases fat burning, making it an excellent drink for those looking to lose weight or maintain a healthy body weight.
- Is matcha tea good for the skin? Yes, the antioxidants in matcha can help protect the skin from UV damage and promote healthy, glowing skin by reducing inflammation and fighting free radicals.